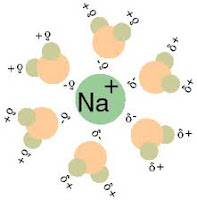
Solution is a homogeneous phases made up of solute and solvent in different ratios. In solution, the solute is dispersed uniformly throughout the solvent. Normally, the component which is in excess is called the solvent and the minor component is the solute. Solvent may be a pure liquid or it may be a mixture of two or more liquids. For example sodium chloride solute is dissolved in water (solvent) forms NaCl solution in aqueous medium. The solution is neutral in nature as it contains equal number of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions.
Solvents containing Hydrogen ion donor groups are called protic solvents. The dielectric constant of these solvents are generally high. Solvent which acts as proton donor and proton acceptors are called amphiprotic solvents . Water, alcohols,amides etc are the best examples for this type of solvent.